Ransomware groups have been concerningly active in recent times, with the two latest attacks targeting an insurance firm and a pharmaceutical company, both in California. The data stolen has put hundreds of individuals at risk and includes documents such as drivers’ licenses, sensitive company financials, non-disclosure agreements and more.
In this article, we’re going to look at everything we know about the attacks so far:
The Crinetics Hack
Crinetics Pharmaceuticals, a clinical-stage biopharmaceutical company, is facing a substantial data leak after being hacked by the ransomware group named LockBit. Although negotiations were underway between the parties for the payment of ransom, they quickly broke down.
The situation started in mid-March as LockBit infiltrated Crinetics' network, stole confidential data, and demanded a $4 million ransom for the deletion of data. During this time, LockBit reinforces that companies should not approach the public if they want to negotiate the deletion of stolen data.
This is where things get tricky – Crinetics acknowledged "suspicious activity" in an employee account and took steps to contain the incident, publicly. They maintained that neither their research databases nor core operations were affected, but LockBit disputes this account.
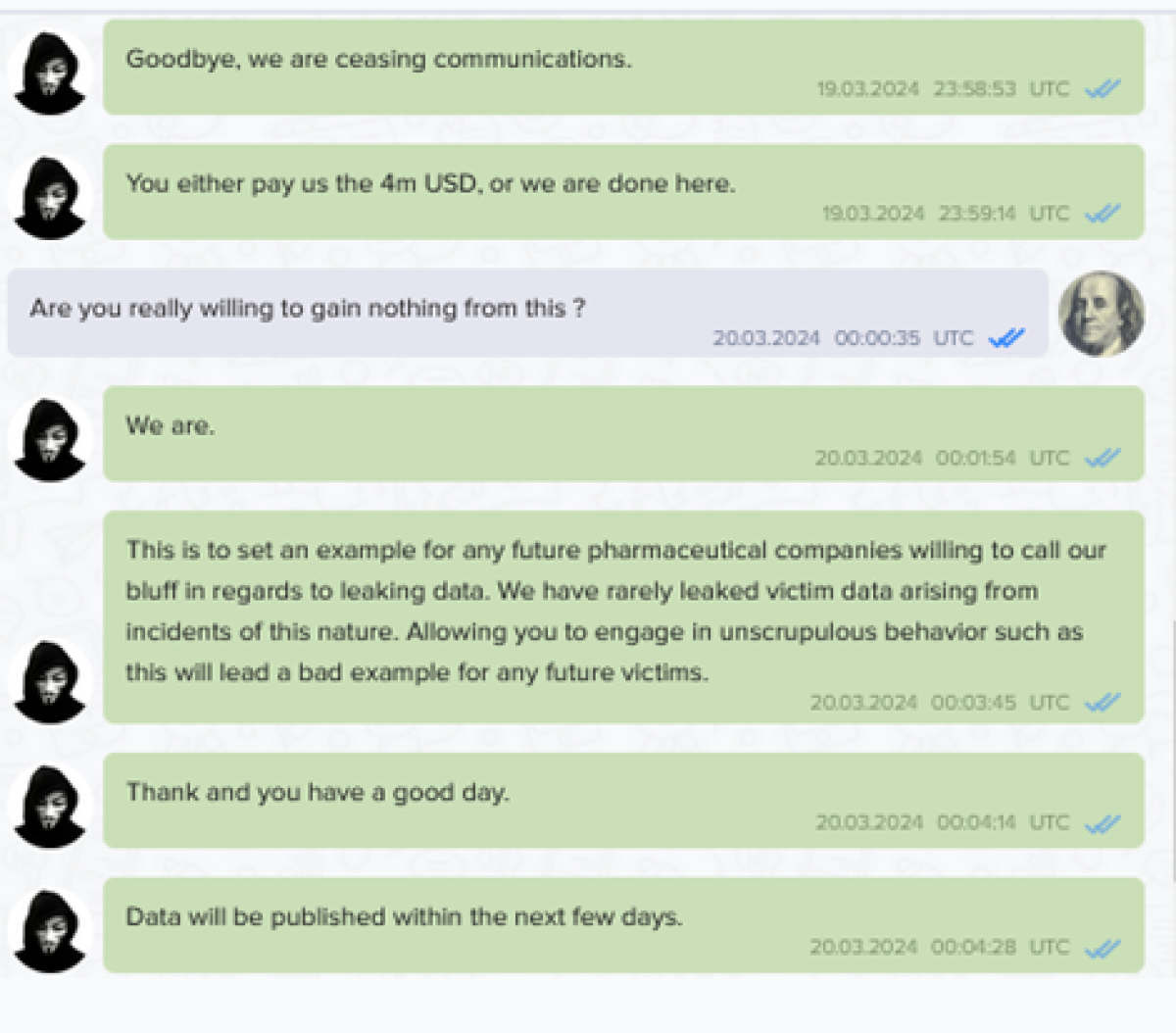
A message thread posted on LockBit’s site.
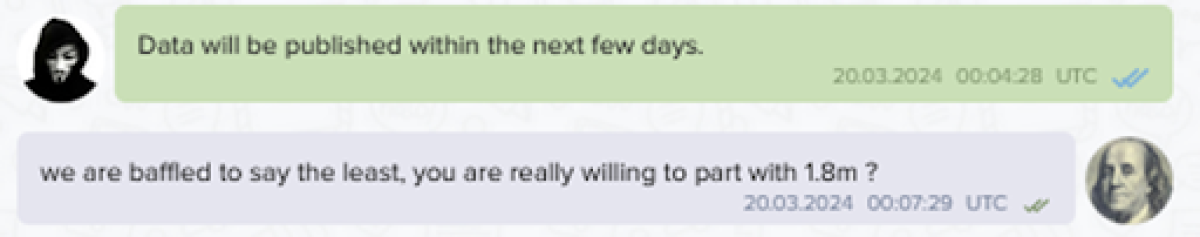
According to the abovementioned message posted on LockBit's leak site, negotiations between the two parties broke down. LockBit accuses Crinetics of "unscrupulous behavior" for speaking to the media about the incident, which they claim violated their terms. Crinetics reportedly offered $1.8 million, which LockBit deemed insufficient.
LockBit has now threatened to publish the stolen data in the coming days. They claim the data is material and will be reported to the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC). LockBit also intends to share the data with Crinetics' competitors and The Humane Society of the United States, citing a 2022 article critical of Crinetics' alleged involvement in animal testing.
The next few days will be crucial as Crinetics grapples with the potential fallout of a data leak. The impact on the company, its investors, and potentially animal welfare research remains to be seen, but will likely be considerably damaging.
The Roberson & Sons Insurance Services Hack
The second victim, Roberson & Sons Insurance Services, is a commercial insurance provider that is also in the midst of a data security crisis after a ransomware attack by the Qilin Group. Qilin claims to have infiltrated Roberson & Sons' network and stolen a significant amount of customer data. On their ransom page, the group states that they have downloaded information on over 2,000 customers, including:
- Sensitive personal details: Social Security Numbers, Driver's License numbers, Dates of Birth
- Vehicle data: Vehicle Identification Numbers (VINs), addresses, mailing information, phone numbers
- Financial information: Taxpayer Identification Numbers, copies of driver's licenses, contracts, insurance payment details, financial documents
Images uploaded on Qilin’s leak website are shown as proof of the attack, we’ve attached one of these that includes the driver’s licenses of three of the victims, with personal details blacked out to respect the victims’ privacy:

Driver’s licenses leaked by the Qilin Group.
Roberson & Sons Insurance Services has not publicly commented on the attack yet. Their website shows no updates regarding the incident.
Judging from the stolen information uploaded, this data breach could have severe consequences for Roberson & Sons' customers. Exposed Social Security Numbers and financial information make them vulnerable to identity theft and fraud from anyone across the world.
Stolen vehicle data could also be used for targeted car thefts or insurance scams within the state. We believe local authorities are likely investigating the incident, but no official statements have been released yet from their side, either.
Moving forward, if you are a customer of Roberson & Sons Insurance Services, we would advise you to be vigilant for any suspicious activity related to your identity or financial accounts. Consider placing a fraud alert on your credit report and monitor your accounts closely.
Who the Ransomware Groups Are
LockBit is a well-established threat actor at this point, having been around since at least 2019. They operate with a Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS) model, essentially providing their attack tools and infrastructure to affiliates who then launch attacks and extort victims. LockBit is known for its aggressive tactics and ruthlessness, as witnessed in this attack.
They employ a double extortion strategy, encrypting a victim's data and stealing it, threatening to release the stolen information if the ransom is not paid. Its targets include a wide range of organizations, from healthcare providers to government agencies.
Qilin, a relatively newer player, having emerged sometime in 2022. Despite their relative youth, they've quickly gained notoriety. Like LockBit, they function as a RaaS group. However, Qilin’s uniqueness comes from its use of Rust (a programming language) for their ransomware, making it as efficient and difficult to detect as possible.
They also target a massive set of victims and are known to customize their attacks for maximum impact. Recent reports, like this one, suggest Qilin's activity is on the rise, particularly in the wake of disruptions faced by other established ransomware groups.
Staying Safe From Ransomware Attacks
The rise of ransomware has made the fortification of your digital defenses crucial in recent times, yet a lot of businesses often overlook this part of their operations. The most critical defense is a strong backup system – back your data up on an external drive or cloud storage disconnected from your main network and do it regularly.
In case of an attack, this makes sure you have a clean copy to restore from. Test your backups periodically to ensure they work properly.
The second biggest culprit is unpatched software – this creates vulnerabilities which act as gateways for ransomware. Keep your operating system, applications, and firmware updated with the latest security patches. Enable automatic updates whenever possible to minimize the window of vulnerability as well. Remember, prevention is always better than cure in the fight against ransomware.


